Chlamydia is one of the most widespread STDs in the world. While it doesn’t always display symptoms, its affects may be severe and irreversible. This disease isn’t known as the silent infection for nothing. It’s considered to be the most prolific STD due to their cunning nature.
Chlamydia is known to utilize the “Trojan horse” tactics to stealthily sneak into host cells. With the help of the Pgp3 protein, it can often evade defenses and avoid detection, making it one of the most prevalent STDs worldwide with over 50 million cases worldwide and approximately 3 million cases in the United States annually.
What is Chlamydia?
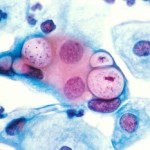 Chlamydia is a very common sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by the bacterium chlamydia trachomatis. The term ‘chlamydia infection’ can also refer to infection caused by any species belonging to the bacterial family Chlamydiaceae.
Chlamydia is a very common sexually transmitted disease (STD) caused by the bacterium chlamydia trachomatis. The term ‘chlamydia infection’ can also refer to infection caused by any species belonging to the bacterial family Chlamydiaceae.
Chlamydia is a major infectious cause of human genital and eye disease. It’s one of the most common sexually transmitted infections worldwide; it is estimated that about 1 million individuals in the United States are infected with chlamydia.
In 2011, approximately 1.4 million cases of chlamydia were reported to CDC from 50 states and the District of Columbia, but an estimated 2.86 million infections occur annually.
A large number of cases are not reported because most people with chlamydia are asymptomatic and do not seek testing.
Chlamydia is most common among young people. Its prevalence among sexually-active young people aged 14-24 years is nearly three times the prevalence among people aged 25-39 years. It is estimated that 1 in 15 sexually active females aged 14-19 years has chlamydia.
How it Spreads

chlamydia baby illustration, image Wikipedia
The bacteria can move from one person to another through sexual intercourse, and possibly through oral–genital contact. If someone touches bodily fluids that contain the bacteria and then touches his or her eye, a chlamydia eye infection is possible.
Chlamydia also can be passed from a mother to her baby while the baby is being delivered. This can cause pneumonia and conjunctivitis, which can become very serious for the baby if it’s not treated.
You can’t catch chlamydia from a towel, doorknob, or toilet seat.
Chlamydia in Men : The Symptoms
It is not easy to tell if you are infected with chlamydia since symptoms are not always apparent. But when they do occur, they are usually noticeable within one to three weeks of contact and can include the following:
• Small amounts of clear or cloudy discharge from the tip of the penis
• Painful urination
• Burning and itching around the opening of the penis
• Pain and swelling around the testicles
Some men have mild symptoms that disappear after two or three days. Even if the symptoms disappear you will still have the infection and be able to pass it on.
Since chlamydia is transmitted through anal and oral sex, men who have sex with other men can contract chlamydia. If you are a sexually active man and you have possible symptoms of chlamydia, being tested is your responsibility.
Complications in Men
original image via: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chlamydia_infection
Complications from chlamydia infection in men are rare. However, if you are sexually active, you can spread the infection to your partner.
If for some reason your chlamydia infection is left untreated, it can sometimes spread and cause long-term problems. Such as:
Urethritis: an inflammation of the urethra that runs along the underside of the penis. It can cause:
• White cloudy discharge from the tip of the penis.
• Pain or a burning sensation when you urinate
• The urge to urinate often
• Irritation and soreness around the tip of the penis
Complications may also include epididymitis: an infection of the epididymis, which is the tube that carries sperm away from the testes, and proctitis: an inflammation of the rectum.
Treatments
Conventional Treatments
If you have chlamydia, your doctor will prescribe oral antibiotics, usually azithromycin or doxycycline. Your doctor will also recommend your partner(s) be treated as well to prevent re-infection and further spread of the disease.
With treatment, the infection should clear up in about a week or two. It is important to finish all of your antibiotics even if you feel better.
Homeopathic Treatment
Apart from the conventional allopathic treatments – homeopathic, herbal and other natural medicines are also available and have been found to be quite effective.
It is possible to bridge the gap between conventional treatments, natural remedies, and all things in between. For an in depth explanation on the various naturopathic drugs and homeopathic herbs used for treating chlamydia. Click on the following link to learn more.
You’ll also have access to preventative measures you can take to minimize your risk of getting Chlamydia, as well as preventing future re-infections.
Educate yourself with the necessary knowledge to combat chlamydia, and get your life back!







 Saving...
Saving...
Latest Comments