Just the other day you remembered going to the doctor’s office to treat your strep throat infection. You were prescribed antibiotics and after taking them you soon began to feel better. However, as you’re taking your medication, you began to notice unusual discharge in your underwear. Your vagina also felt very itchy.
You decided to ask your doctor about this. Your doctor then diagnosed you with a vaginal yeast infection. He also told you that yeast infection can be a side effect of taking antibiotics, and the treatment for yeast infection is usually quick and easy.
What Is a Yeast Infection?
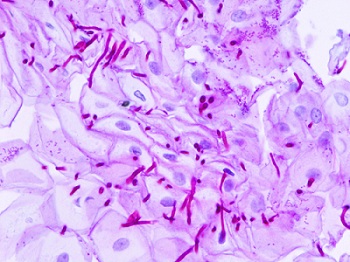 A yeast infection, also known as candidiasis, is the name for a common infection caused by a yeast called candida albicans, which is a type of fungus.
A yeast infection, also known as candidiasis, is the name for a common infection caused by a yeast called candida albicans, which is a type of fungus.
These fungi are found almost everywhere in the environment. Some may live harmlessly along with the abundant ‘native’ species of bacteria that normally colonize the mouth, gastrointestinal tract and vagina.
Usually, Candida is kept under control by the native bacteria and by the body’s immune defenses. If the mix of native bacteria is changed by antibiotics, the body moisture that surrounds native bacteria can also have subtle changes in its acidity or chemistry. This can cause yeast to grow and to stick to surfaces, so that the yeast causes symptoms.
Candida infections can cause occasional symptoms in healthy people. If a person’s immune system is weakened by illness such as AIDS or diabetes, malnutrition, or certain medications, candida fungi can cause symptoms more frequently.
Candidiasis can affect many parts of the body, causing localized infections or larger illness, depending on the person and his or her general health.
Types of candidiasis
Types of candidiasis include:
- Thrush. Thrush is the common name for a mouth infection caused by the Candida albicans fungus. It affects moist surfaces around the lips, inside the cheeks, and on the tongue and palate. Thrush is common in people with diseases such as cancer and AIDS, which both suppress the immune system. Thrush can develop in people with normal immune systems, too, particularly in people with diabetes or long-lasting irritation from dentures.
- Cutaneous or skin candidiasis. Candida can cause skin infections, including diaper rash, in areas of skin that receive little ventilation and are unusually moist.
- Vaginal yeast infections. Vaginal yeast infections are not usually transmitted sexually. During a lifetime, 75% of all women are likely to have at least one vaginal Candida infection, and up to 45% have 2 or more. Women may be more susceptible to vaginal yeast infections if they are pregnant or have diabetes. The use of antibiotics or birth control pills can promote yeast infections. So can frequent douching.
Symptoms and treatment depend on which part of the body is infected.
Thrush: Thrush causes curd-like white patches inside the mouth, especially on the tongue and palate and around the lips. If you try to scrape off this whitish surface, you will usually find a red, inflamed area, which may bleed slightly. There may be cracked, red, moist areas of skin at the corners of the mouth. Sometimes thrush patches are painful, but often they are not.
Cutaneous candidiasis: Cutaneous candidiasis causes patches of red, moist, weepy skin, sometimes with small pustules nearby.
Vaginal yeast infections.: Vaginal yeast infections may cause the following symptoms: vaginal itch and/or soreness; a thick vaginal discharge with a texture like soft or cottage cheese; a burning discomfort around the vaginal opening, especially if urine touches the area; and pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Yeast Infection in men
Men can get an infection of the head of the penis that is caused by the same candida that causes vaginal infections in women. Men who have diabetes or are on antibiotics for a long time are more prone to this infection.
A man with a yeast infection may not have any symptoms or the tip of the penis may become red and sore or itchy. Some might have a slight discharge or pain with urination as well.
Also, men who are not circumcised need to take extra care to clean properly beneath their foreskins. The warm, moist folds of the foreskin are the perfect environment for yeast to thrive. Keeping the area clean and dry may help prevent an infection, but if symptoms do show up, a trip to the doctor will treat the infection.
Complications: Invasive Yeast Infection
If candida yeast gets into your bloodstream, it can spread to other parts of the body. This type of infection is also called candidemia.
This infection may happen if you have a weakened immune system and a yeast infection goes untreated. Or it may occur if you come in contact with medical equipment contaminated by the fungus.
Symptoms of an invasive yeast infection can be vague and depend on which part of the body is affected. Common symptoms include fever and chills that continue after you have taken antibiotics.
This type of infection is more often seen in people who are or have been in the hospital. It is a leading cause of bloodstream infections and death in hospitalized patients.
You are more likely to get this type of infection if you:
• Are in the hospital’s intensive care unit (ICU)
• Have had recent surgery
• Have a central line (catheter)
• Have a weakened immune system
Very low-birth-weight infants also have a higher risk for this type of infection.
Invasive candidiasis is a very serious condition that requires prompt treatment. You will be given antifungal medicine by mouth or through an IV for several weeks.
Prevention
In general, you can prevent most Candida infections by keeping your skin clean and dry, by using antibiotics only as directed, and by following a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition. People with diabetes should try to keep their blood sugar under tight control.
If you have HIV or another cause of recurrent episodes of thrush, then antifungal drugs can help to minimize flare-ups.
Conventional Treatments
Treating a yeast infection is simple. But it’s still important to visit your doctor for the right diagnosis, since other infections can cause similar symptoms but require different treatments. Your doctor might take a urine sample — to rule out a urinary tract infection — and swab some discharge from your vagina to examine under a microscope.
In case of a yeast infection, your doctor will probably prescribe a pill to swallow or a cream, tablet, or suppository to put in the vagina. All of these types of medication can clear up your symptoms in a couple of days and cure the infection within a week.
Natural treatments
Apart from the conventional treatment methods described above, a holistic and natural system of eliminating yeast infection is available.
Curing yeast infection has to be achieved by tackling all of the many factors responsible for Yeast Infection. While one-dimensional treatment like antibiotics, pills, creams, anti-fungals or even detox may alleviate the symptoms, they only tackle one aspect of the disease.







 Saving...
Saving...
Pingback: Tea Tree Oil, Home Remedy for Yeast Infection - STDZip.com